Latest News and Resources
Too Small for IT Security? Data Says Think Again! Attacks on SMB Rise
Is Your Organization at Risk? If You Run Your Business Without Strategic IT Security, the Answer is…
For many small business owners IT security planning can seem like a luxury, but a lack of proactive security can actively hamper growth, even among the smallest of businesses.At its worst, not having the right defenses in place can sink your business operations as your entire enterprise is brought to a standstill by a malicious attack.

Many small- and medium-business owners know that IT security is something they should care about, but they have no idea how to manage it. One study by the National Cyber Security Alliance found that a whopping 59 percent of small business owners have no plan in place to prevent data breaches.
Even industries that revolve around preparing for the worst can be affected. IT help desk services can often be the first the line of defense for insurance companies, financial services firms, and healthcare providers in San Francisco, Oakland, or elsewhere throughout the greater Bay Area.
In fact, insurance companies are one example where a lack of network support services might have an outsized impact. Insurance companies regularly deal with highly sensitive data, including names, Social Security numbers, birthdays and addresses. Having the right IT support is essential.
What’s at Stake
The cost of data breaches can be enormous for small business owners. Research from Atlanta-based payment technology firm First Data shows that as many as 90 percent of data breaches can be traced back to small businesses, and the average cost of a breach to small businesses can be as high as $50,000 or more.

Not only would the cost of a malicious cyber attack or data breach be devastating for most small businesses, but the these costs and don’t even begin to account for the cost associated with the loss of trust from your customers.
Working with the right IT support firm to address the security, continuity and disaster recovery needs of your business are all critical to successfully maintaining and protecting your organization.
What Companies Can Do
Experts say that, at the very least, small businesses can enact the following controls:
- Secure all your business data. Security experts at Kroll say businesses should only keep the data they need.
- Stay current with security patches and updates. This can be more difficult than it seems, especially for busy small businesses.
- Require the strongest possible passwords.
- Establish an Internet usage document and make employees sign it.
- Limit access to your network outside of private workspaces.
- Consider a professional IT security audit.
Looking Inward
No one wants to think about a worst-case scenario, but threats to business data aren’t likely to go away any time soon. Unfortunately, employees are often at unwittingly at the center of them. Data from TrendMicro found that nearly 60 percent of employees surveyed “very frequently or frequently stored sensitive data on their laptops, smartphones, tablets, and other mobile devices.”
This may mean that more sophisticated IT support is needed to prevent a worst-case scenario in the era of Bring Your Own Device (BYOD). Rather than relying on stop-gap measures, an ounce of prevention may secure your business now and in the future.
If you are looking to get started in addressing your IT security concerns or looking to implement a strategic business technology plan for your organization, look no further and contact Bay Computing to get your complimentary onsite assessment started today.
Read More
How Does HIPAA Affect Healthcare IT in California
HIPAA’s Impact on Your Healthcare IT Operations
Back in 1996, HIPAA (Healthcare Portability and Accountability Act) was established and enacted to protect the private health information of patients, to facilitate health record transfers between companies, to create standards regarding electronic billing and patient information, and to introduce fraud reduction.
Without Healthcare IT Support, This Ends Up Happening Far Too Often …

In California, the California Department of Health Care Services oversees compliance through the Office of HIPAA Compliance.Electronic health records, electronic billing and other emerging technologies allow your practice to focus on providing quality health care instead of wading through paperwork or chasing down insurance companies, but ensuring your IT health solutions stay in compliance can be challenging. Data security, unauthorized access and wireless device factors are a few IT issues your practice can face.
Data Security Measures
One of the biggest concerns with staying compliant is how non-specific HIPAA technical security regulations are. The HIPAA regulations are written without specifying exactly which technology you need in order to allow for flexibility in choosing innovative technology, but the flipside is that there’s lots of room for interpretation.
The regulations don’t require a specific type of technology as long as the technical solution used adheres to several security guidelines. This regulation can lead to confusion if your practice isn’t accustomed to handling IT security solutions. Major areas covered by these regulations include access control, audit control, integrity, person or identity authentication, and transmission security.
Connected Devices
Another HIPAA challenge practitioners in the California Bay Area face is factoring in connected devices on the network, whether these are medical devices with connectivity or tablets and mobile smartphones. Devices with access to the network need to meet certain security standards in order to completely comply with HIPAA. It takes time to work through the appropriate security measures on your own, especially if you have many types of mobile devices falling under management.
Outsourced healthcare IT services are an extra resource you can use to help manage these devices, whether they actively monitor the network or offer suggestions on appropriate mobile access solutions.
Electronic Health Records Solutions
Electronic health records cut down on your medical paperwork requirements, streamline patient intake processes and provides you with a comprehensive view into a patient’s medical history. However, choosing the right EHR solution can be a frustrating task, as there are many options on the market.
Working with Healthcare IT service support specialists benefits your medical practice by leveraging their knowledge on available solutions so you don’t choose the first one that presents itself. These services often work with multiple EHR solutions for hands-on experience instead of reading features off a data sheet.
Healthcare technology is intended to help you focus on what you do best: provide quality health care to your patients. If you’re mired in regulations and technology procurement, you don’t get to focus on your core goals. While you theoretically can learn everything you need to know about medical technology and HIPAA technical requirements, your focus has always been and always will be on providing the best patient care.
Outsourcing your technology support needs to a trusted IT service provider partner allows you to use your time and resources the most effectively for the unique needs of your practice.
If you’re curious to learn more or looking to get started but feeling overwhelmed, contact Bay Computing for your free onsite consultation and we’ll get your technology back on the road to recovery today!
Healthcare Providers 450% More Likely to Be Blackmailed by Cryptowall – How to Protect Yourself
Healthcare Providers Beware: Cybercriminals Targeting Covered Entitites (CE) with Malware and Data Breaches
The cyber crime landscape is rapidly growing more dangerous and complex for organizations of all sizes. Reports of security incidents are growing 66 percent each year, with the average cost of a data breach estimated at $3.5 million.
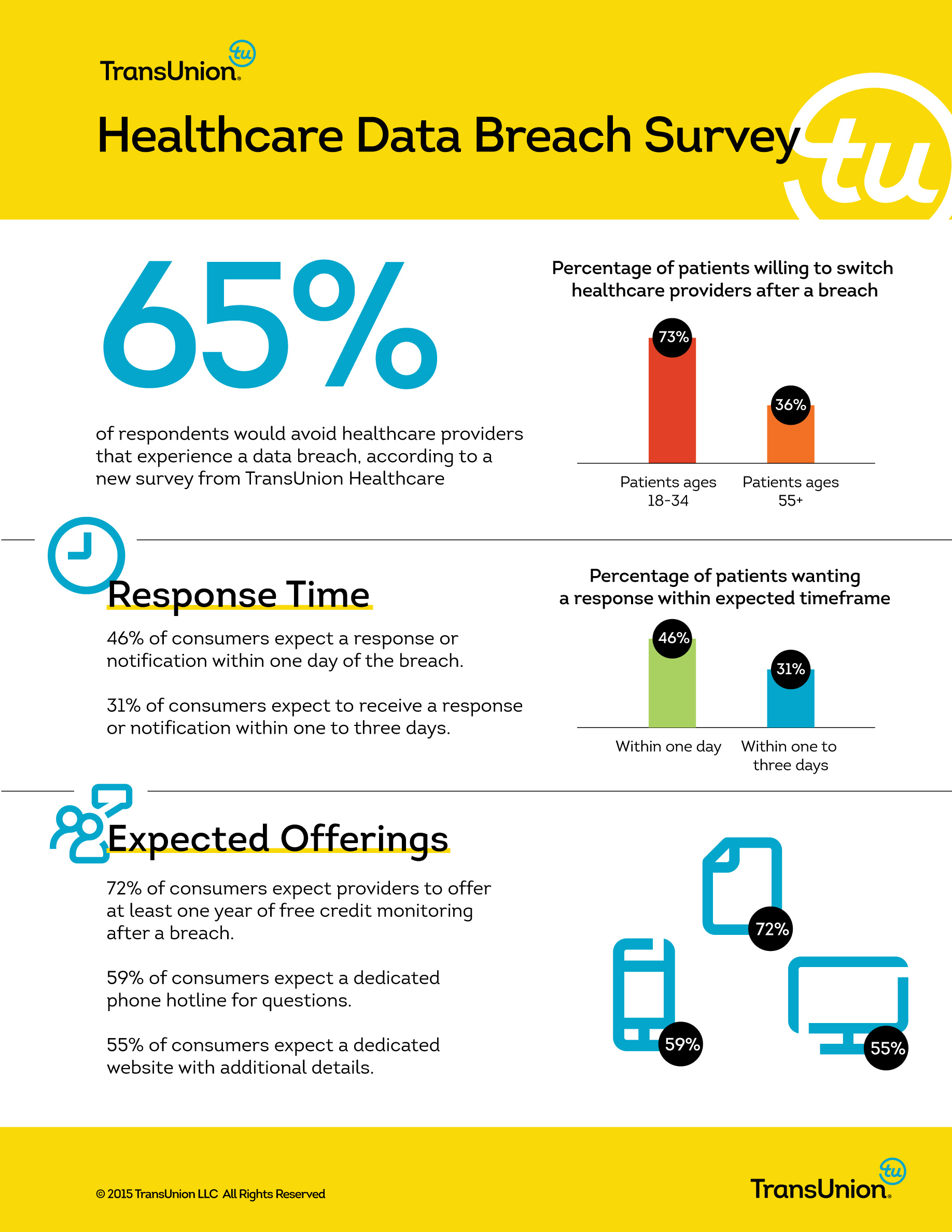
While organizations in any industry are at risk of cyber crime from outside attacks or insider perpetration, many small and medium-sized businesses (SMB) lack the infrastructure to adequately plan and prepare defenses for common threats. One rapidly growing information security threat that repeatedly poses a threat is Cryptowall, a increasingly common form of ransomware.
What is Cryptowall?
Cryptowall, formerly known as Trojan.Cryptowall, is a “Trojan Horse” virus that encrypts files on an infected computer. To unlock the files and retrieve access to critical information, users are asked to pay a “ransom” of at least several hundred dollars via a text document message. The attackers commonly ask for the payment to be made in Bitcoins, and direct users to complete the payment online via a secure Tor browser. In many cases, the ransom demands can increase in amount if the fee isn’t paid quickly.
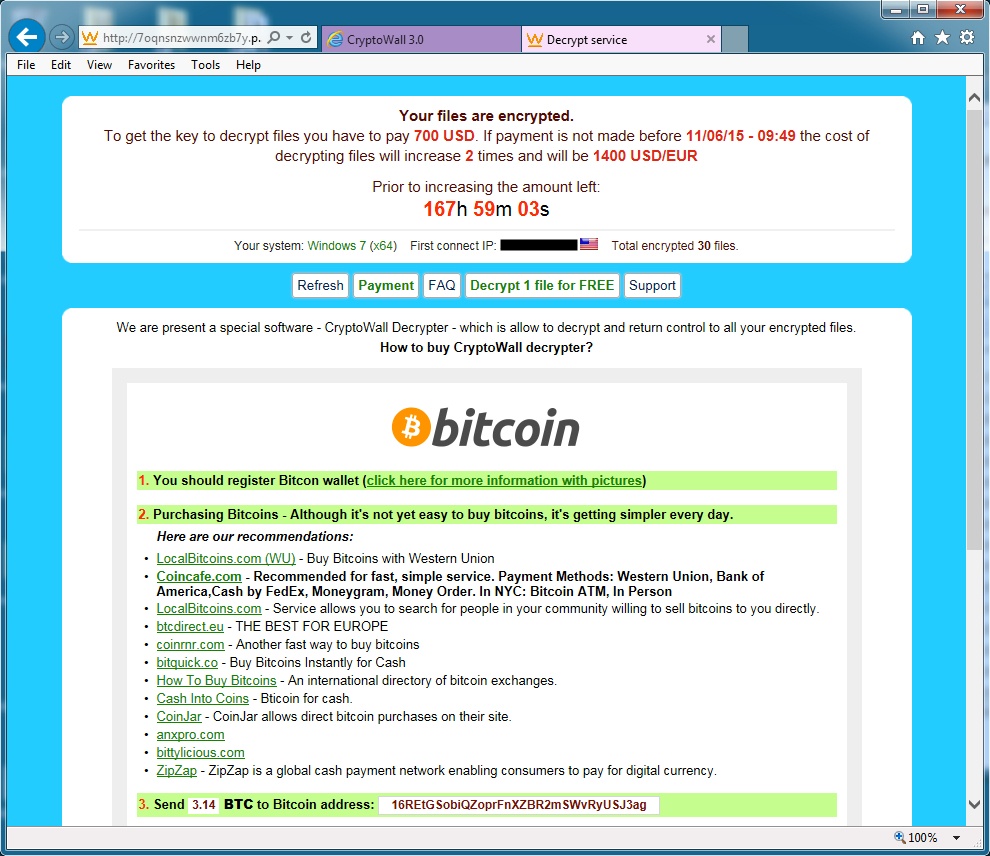
If you’re curious whether someone on your staff with above-average computer skills can unlock your files, the answer is unfortunately no. As soon as files are encrypted, much like a bank vault, they will then require a key to be unlocked… And that key is what must be purchased from the cybercriminals themselves.
The head of cyber security at the US FBI recently stated that he usually advises victims of Cryptowall and other forms of ransomware to “just pay the ransom.” The FBI has yet to find a definitive solution to Cryptowall because it’s a highly effective form of extorting money out of healthcare organizations, SMBs and other companies.
How Do I Prevent a Cryptowall Attack?
The single most important action companies of any size can take to prevent terrible repercussions from a ransomware attack is regular data backups. Keep in mind, Cryptowall will also lock up data on any mapped drives, including external hard drives. The only guaranteed way to keep your information safe is investing in a secure, comprehensive backup solution that won’t be affected by the virus. (Keep in mind that the intervals of regular, ongoing backups can also be crucial to minimizing data loss).
Ransomware viruses can enter a company through a number of means, including file-sharing, email and RDP ports. While training your employees on information security best practices can protect against phishing attacks or unsafe file downloads, the most important step you can take is to develop a comprehensive information security practice and policy. By partnering with a professional IT services firm, you can benefit from having easy access to a dedicated a team of experts who are committed to keeping your patients, providers and practice safe.
Conclusion
Cryptowall attacks can have a devastating impact on healthcare providers and covered entity organizations of any size.
By working stategically with a dedicated IT services team, you can get started implementing the right defensive strategies to help protect your patients, practice and sensitive data such as PHI.
Get started on your data security roadmap with the healthcare information technology experts of San Francisco today with your free onsite technology assessment and rest easier knowing your patients’ data is protected from being held ransom by cybercriminals.
Read MoreAre Your Office Operations HIPPA Friendly? Improving Patient Care and Protecting PHI
How HIPAA Affects Office IT, the Business Operations of Healthcare Providers and Overall Patient Care
From its inception, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) has had many ramifications for healthcare providers, and when it comes to technology management and IT support, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed.
When HIPAA affects how and where your office utilizes its IT devices and systems, your business operation methods and the manner in which patients are cared for. This is a brief look at some of the ways HIPAA may modify the workings of your healthcare enterprise.

Protecting Your IT Devices
Your IT provider’s healthcare IT help desk service in the Bay Area can inform you about procedures such as data encryption and decryption, unique user identification and audit controls, all of which are required under HIPAA. But physically safeguarding workstations that have access to electronic protected health information (ePHI) is also a requirement.
Reception areas are one of the places where inadvertent disclosure of PHI may occur, and simple solutions such as privacy panels at right angles to the reception and scheduling counters, and asking queuing patients to stand away from the worktops, are all that may be needed.
Furthermore, when computer monitors are used in open-bay setups (such as dentists’ chairs), best practices require that care be taken to ensure that screens displaying patient information are not left facing other patients or passing foot traffic.
Who You Do Business With
HIPAA regulations not only cover your healthcare organization (known as a covered entity), but your Business Associates (BA). These are entities or individuals who you may release PHI to, including attorneys, accountants, cloud storage companies, web hosts, IT vendors, email encryption companies, consultants and healthcare clearing houses who deal with claims. As part of your path to harmony with HIPAA, you and your BAs are required to sign a Business Associate Agreement (BAA).
Navigating Office Administration While Caring for Patients
Regular routines are also affected by HIPAA regulations. For example, what happens with standard appointment reminders?
The University of Texas Health Science Center states that as long as patients are aware of this routine and the reminders are generic in form, that is, don’t necessarily state the name of the practice or clinic, appointment prompts are allowed under HIPAA. The same applies to sign-in logs in reception areas: no confidential medical information should be listed.
Helping your office navigate HIPAA-related Healthcare IT solutions are one of the specialties of Bay Computing– So get in touch with the Bay Area team of experts today and schedule a free onsite assessment to get your strategic technology plan started!
Read MoreDyre Malware Has Stolen Over $1 Billion: Is Your Company’s Sensitive Data at Risk?
As Cyberattacks Continue to Skyrocket, DYRE Malware Grew 125% in Q2 Alone. Are You Prepared for the Latest?
Both consumers and organizations of all sizes are at increased risk for DYRE malware attacks in the months to come. TrendLabs reported a 125 percent increase in DYRE attacks in the second quarter of 2015, proving that criminal interest in stealing user credentials is growing.
Simultaneously, attacks against healthcare organizations have grown 600 percent, and these organizations are 74 percent more likely to be targeted by phishing emails than other industries.
Despite the increased climate of threats, small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) can take the right steps to protect their finances and their customers’ sensitive data against DYRE and other phishing attacks.
What Is DYRE Malware?
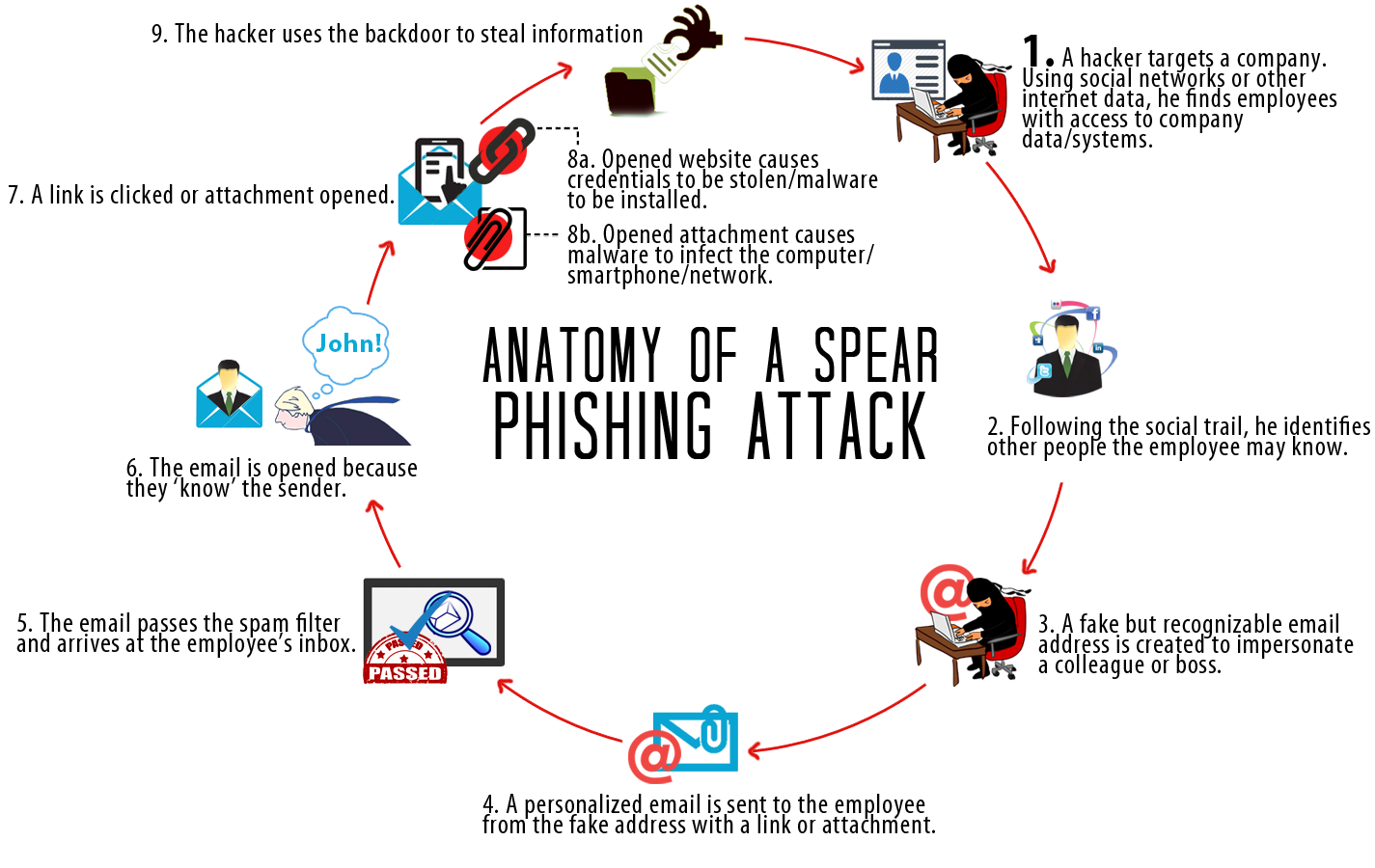
DYRE malware typically enters a business network through a phishing email, which is designed to look like an important communication from a bank, the IRS, or another business entity. An example shared by TrendLabs included a subject line pertaining to a tax levy and an important-looking attachment with body copy that indicated immediate action was necessary. When employees click the link in the body of the email or open the attachment, the malware gains access to the system.
What Are the Repercussions of a DYRE Attack?
DYRE works quickly once it gains entry and performs “man in the middle attacks.” According to TrendMicro, it may perform browser screenshots and steal personal certificates to obtain password credentials to protected information. DYRE also works to avoid detection by disabling information security measures organizations may already have put into place, including firewalls and anti-malware protections.
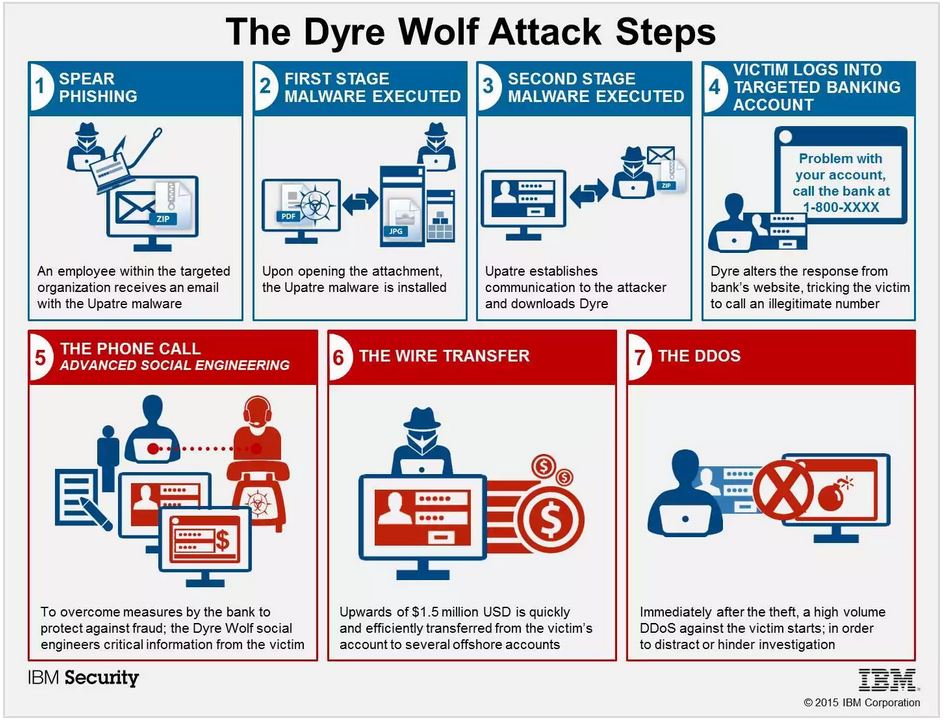
Among private consumers, DYRE attacks are typically focused on stealing banking credentials so cybercriminals can gain access to an individual’s money. In healthcare organizations, the focus is usually to obtain protected patient or customer information so identities can be resold at a profit or ransomed back to the victim.
How to Protect Yourself Against DYRE and Other Phishing Attacks
To prevent a DYRE attack, phishing awareness among your employees is critical. A full-featured anti-malware solution and password change policies can help organizations get started protecting against the “dire” effects of this unfortunate information security trend.
In order to stay safe, all individuals at your organization need to be aware of how to detect a potential email attack, and who to notify if an email ever appears suspect… And for many small and medium businesses and practices, identifying the right resource to reach out to for technical help may not always be clear.
Despite increased threats, information security for SMBs and healthcare organizations isn’t impossible. Working with an expert managed services provider with years of experience helping with strategic information security enables you to identify your organization’s primary vulnerabilities, establish much-needed policies, and perform ongoing training to allow you to avoid the costly cleanup and customer defection that follows a major cyberattack.
Read More10 Mind-Blowing Facts on the State of Information Security for Small Business in 2015
Information security (IS) should be a key priority at organizations of any size. Gartner reports the average company dedicates just five percent of its budget to protecting customer data.

The staggering costs of a cybercrime attack can be particularly devastating to small and mid-sized businesses (SMB). Gain insight into the state of cybercrime and what SMB need to know to protect themselves.
1. Attacks Are Increasing
Despite companies’ increased efforts to protect themselves against crime, the rate of incidents continues to grow. The annual compounded growth rate of cybercrime is 66 percent.
2. Most Companies Are Unprepared
The average business doesn’t feel prepared for the current IS climate. In fact, 56 percent doubt they would even be able to detect a sophisticated attack.
3. Vendors Are Ignored
Many SMBs fail to realize that vendor security issues can lead to risks. Perhaps more concerning, 33 percent are not sure if they have a security agreement in place with their vendors.
4. Your Employees Are a Risk
Data breaches can occur due to cybercriminals, but the vast majority of security incidents are caused by employees. In many cases, this is due to a lack of knowledge on security best practices.
5. Companies Are Spending More
Sixty-two percent of companies of all sizes are choosing to proactively protect themselves against risks by spending more of their IT budgets on security, which can include bringing on professional help by working with a professional IT services provider.
6. Attacks Are Very Expensive
The average security attack worldwide costs $3.5 million dollars, which can cover the costs associated with fines, fees, notifying customers, and related charges. Each lost or stolen customer identity comes to around $145.
7. Companies Aren’t Testing Enough
Forty-nine percent of companies fail to complete “fire drills” to determine just how effective their data recovery practices, encryption, and other components of information security really are.
8. Mobile Is Risky
The rising adoption of smartphones and tablets doesn’t mean it’s safe. Mobile device management and Mobile vulnerabilities are currently considered the single-biggest security risk, especially since employees may take these mobile devices off site or connect to unsecured wireless networks.
9. Policies Matter
Despite the importance of educating employees, only 76 percent of brands have password policies developed and company-wide procedures in place.
10. IT Is Concerned
Eighty percent of IT professionals believe their organizations need to be working harder to defend against cybercrime. In many cases, these professionals are limited by budget and company culture.
Taking steps to protect your customers’ data could be the best IT investment you make this year. In an era of increased cybercrime, employee education, security technologies, and increased vigilance aren’t just important. They’re necessary.
Get in touch with your local San Francisco Bay Area Managed Services Provider to get started on your strategic information security roadmap today!
Read MoreNew Malware can infect your FitBit and spread to your computer
Could Your Wearable Carry Viruses?
Recently, a type of vulnerability
Infecting a Fitbit via Bluetooth Is Possible
Hackers
How to Protect Your Devices From Malware
To prevent malware infection,
Although the Fitbit virus is merely hypothetical
Reach out to your Bay Area IT support team and get your network security road map started a with a free onsite network assessment today!
Stegoloader Malware Sneak Attack Hits California Healthcare Providers
Stegoloader Malware Targeting Healthcare Providers Throughout California—Is Your Practice Safe?
There have been number of reports about how stegoloader malware is being used to target healthcare providers across North America, which is increasingly becoming a cause for concern for many practitioners.
Why? Stegoloader malware is the latest and most disastrous version of TROJ_GATAK, (the strain of trojans which use steganography to evade detection) and is sophisticated enough to conceal itself and often slips by undetected because of this ability.
Stegoloader Trojan Infection Count Per Industry
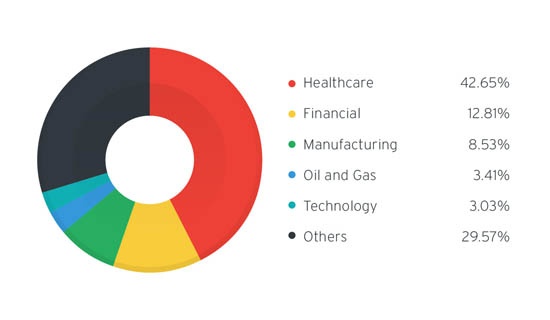
In order to avoid becoming an easy target many healtcare providers throughout the San Francisco Bay Area are choosing to partner up with seasoned IT support teams who have the security skills necessary to protect them against the latest generation of advanced malware.
Read on if you work in healthcare, deal with PHI, and want to learn more about how to keep your organization safe.
Just What Is Stegoloader Malware?
Stegoloader is advanced malware that utilizes digital steganography by hiding within a Portable Network Graphic (PNG) hosted on a valid website. Once this malware is accidentally accessed, it remains on the computer, lurking in the background, often evading detection.
It should be noted that the malware is so sophisticated that when it detects security or analysis tools running on the infected system, it will suspend its main program code, allowing it to stay hidden. Furthermore, it has been designed to ‘look’ for reverse engineering tools and terminate them, making it difficult for providers to regain control of their computer systems even when a security threat has been identified.
North American Healthcare Providers Targeted
A report carried out by Trend Micro found that North American healthcare providers were by far the greatest targets and experienced the heaviest impact as they became infected with the Stegoloader Trojan.
It increasingly appears that cyber criminals are becoming more interested in stealing healthcare information than even credit card information (PCI) since protected health (PHI) information has been fetching higher prices on the black market. This puts healthcare providers in a vulnerable position as their system security may have been breached without them even being aware of it.
Keeping Your Organization Safe
Stegoloader malware is impacting healthcare providers across North America. Up until they experienced a breach directly, many of these organizations remained complacent as business operations demanded full attention and the priority of planning IT security was set aside.
Don’t make the same mistake by assuming you have the adequate security measures in place. If you are concerned that your healthcare practice may have already been targeted, or want to prevent your system security from being infiltrated, get started with a free network assessment today.
Leverage the wealth of experience of our strategically-minded IT support services team, and implement the right technological solutions for your office to help prevent your organization from falling vicitm to a healthcare data security breach.
Is your point of sale software at risk of being infected by malware?
Is Your Point of Sale Software At Risk of Being Infected by Malware?
Point
What Is Point of Sale Malware?
Malware
Some of the high-profile companies that have
How to Protect Your Business
The first step to protecting
At
Essential Facts About the Cloud for Business Owners
5 Essential Facts About the Cloud for Business Owners
Cloud computing
1.
The most attractive thing about Cloud systems
2. The
Because everything is hosted
3. Cloud-Based Systems May Have Tighter Security Than In-House Solutions Due to Compliance Regulations
Some businesses are wary of Cloud-based
4. There is No Upgrade Cycle for SaaS.
One of the drawbacks of in-house software is the constant need to upgrade to the latest version. Sometimes
5. Switching to the Cloud Can Enable Next-Generation Analytics.
The other buzzwords you may have heard
Cloud computing
http://www.economist.com/news/business/21648685-cloud-computing-prices-keep-falling-whole-it-business-will-change-cheap-convenient
